LC/MS/MS Method Package for Lipid Mediators Ver. 3
Описание
For LabSolutions™ LCMS
Ready-to-Use Analytical Conditions
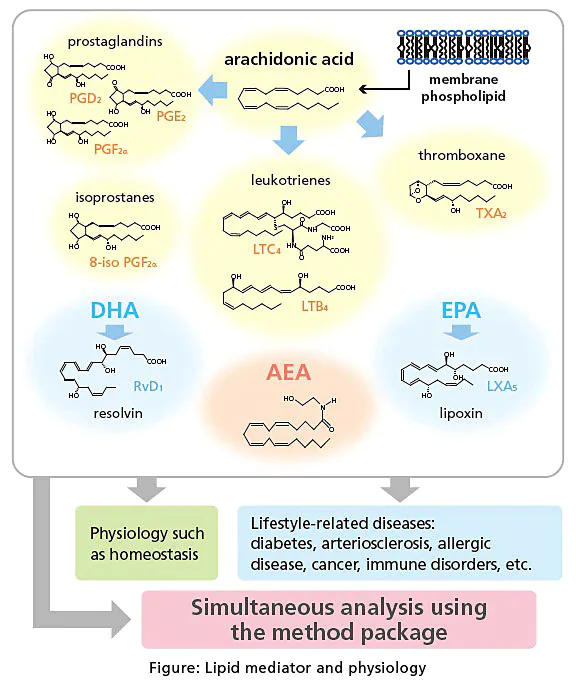
Lipid mediators (bioactive lipids) have important physiological functions and have been associated with allergies, thrombosis and lifestyle-related diseases. This method package provides a simultaneous analysis method that encompasses totally 214 compounds, which include 196 compounds of lipid mediators derived from arachidonic acid cascade and 18 internal standard compounds.
Retention Time Correcting Tool Supports Identification of Isomers
The Retention Time Correcting Tool available in this version simplifies retention time correction, enabling precise identification of isomers that cannot be distinguished by MRM. The 196 compounds are divided into 18 groups based on their properties, and internal standard samples have been chosen for each group, making it possible to correct for quantitation errors that may arise, such as during solid phase extraction.
UFMS Technology Covers a Wide Range of Compound Groups
Fatty acids are usually detected with ESI-, but for a few important lipid mediators such as anandamide (AEA), ESI+ is preferred. Conventional joint analysis methods use only unipolar analysis. But the LCMS-8060 is capable of high-speed polarity reversal in just 5 ms, allowing many more types of compounds to be analyzed simultaneously. Compounds listed for joint analysis include 100 arachidonic acid derivatives, 26 EPA derivatives, 23 DHA derivatives, 11 ethanolamides, and 36 others, including other fatty acid metabolites and platelet-activating factor (PAF).
Category codes
LA : linoleic acid
ALA : α-linolenic acid
EDA : eicosadienoic acid
AA : arachidonic acid
ADA : adrenic acid
DGLA : dihomo-γ-linolenic acid
EPA : eicosapentaenoic acid
DHA : docosahexaenoic acid
EA : ethanolamide
ISTD : internal standard
Remarks and Precautions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
LabSolutions LCMS Ver. 5.93 or later is required.
Shimadzu makes no warranty regarding the accuracy of information included in the database or the usefulness of information obtained from using the database.